We offer a comprehensive line of vascular access products that help to ensure you have the right vascular access device for each and every patient. These products are available in a variety of sizes and design configurations.
> To jump to a specific product webpage quickly, use the buttons below.
View each product’s Instructions for Use, specifications, components, and other resources by clicking the links below.
Infections hurt your patients, your HAC score, your bottom line, and much more. Help is here with Cook Spectrum technology.
 The right combination
The right combination
Cook Spectrum catheters are impregnated with a combination of the antibiotics minocycline and rifampin in order to help patients by providing proven protection against catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs).¹
 Unmatched evidence
Unmatched evidence
The efficacy of Cook Spectrum is supported by more than 30 sources published over the past two decades, including peer-reviewed studies and meta-analyses.
 No evidence of increased resistance
No evidence of increased resistance
More than 10 years of clinical use and a 7-year study of more than 500,000 Cook Spectrum catheter days have shown no evidence of increased antibiotic resistance.²
 Worth switching
Worth switching
Switching from unimpregnated catheters to Cook Spectrum catheters helps provide quality patient care by decreasing the risk for CRBSIs and the costs associated with treating them.1,3
View a comprehensive list of Cook Medical products that have Cook Spectrum technology.
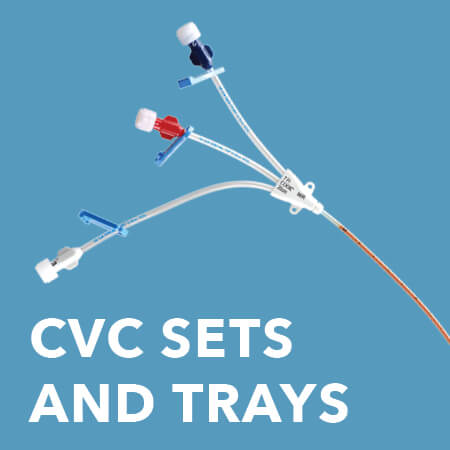
 CVC sets and trays
CVC sets and trays
〉Available with or without Cook Spectrum technology
Used for treatment of critically ill patients and suggested for continuous or intermittent drug infusions; central venous blood pressure monitoring (CVP); acute hyperalimentation; blood sampling; delivery of whole blood or blood products; and simultaneous, separate infusion of drugs.
Features and benefits
• Cook Spectrum central venous catheters (CVCs) provide patients with proven protection against CRBSIs.1
• Power-injectable (CT) options are available; “CT” is printed on the distal lumen.
• Depth markings every 1 cm help you insert the acute CVC accurately.
• Maximum flow rates are printed on the lumen clamps.
• The polyurethane material is designed for pushability and high flow rates.
• A wide variety of sizes maximizes your procedural options.
View more details about CVC sets and trays and Cook Spectrum CVCs.
 Dieckmann Intraosseous Infusion Needle
Dieckmann Intraosseous Infusion Needle
Used as an alternative to intravenous access during pediatric emergencies, permitting the infusion of drugs and fluids.
Features and benefits
• Two laterally opposed sideports positioned near the needle cannula’s distal tip ensure proper flow if the needle tip is obstructed by posterior bone cortex.
• The positioning mark that is 1 cm proximal to the needle cannula’s distal tip provides a visual reference point for depth determination.
View more details about the Dieckmann Intraosseous Infusion Needle.
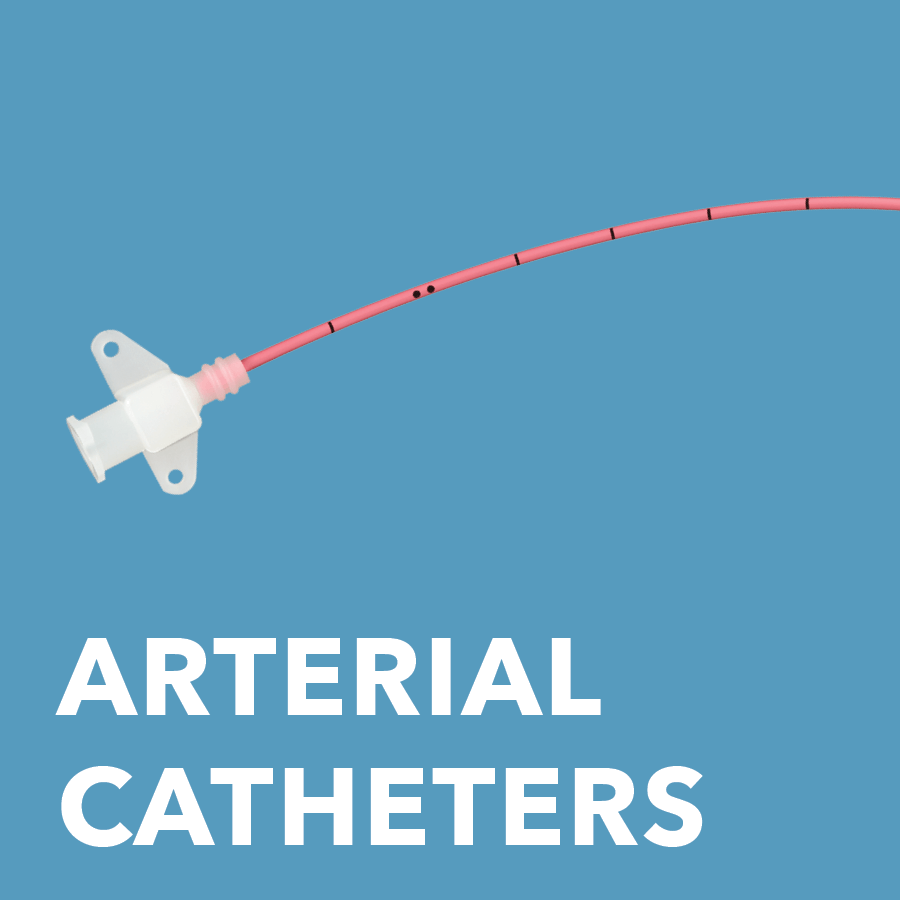
 Arterial Pressure Monitoring Sets and Trays
Arterial Pressure Monitoring Sets and Trays
Used for arterial pressure monitoring and blood sampling.
View more details about Arterial Pressure Monitoring Sets and Trays.
 Bunegin-Albin Air Aspiration Set
Bunegin-Albin Air Aspiration Set
Used for the retrieval of venous air emboli.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The entire catheter is radiopaque in order to maximize visibility during placement under an x-ray.
View more details about the Bunegin-Albin Air Aspiration Set.
1. Raad I, Darouiche R, Dupuis J, et al. Central venous catheters coated with minocycline and rifampin for the prevention of catheter-related colonization and bloodstream infections: a randomized, double-blind trial. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(4):267-274.
2. Ramos ER, Reitzel R, Jiang Y, et al. Clinical effectiveness and risk of emerging resistance associated with prolonged use of antibiotic-impregnated catheters: more than 0.5 million catheter days and 7 years of clinical experience. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(2):245-251.
3. Zimlichman E, Henderson D, Tamir O, et al. Health care-associated infections: a meta-analysis of costs and financial impact on the US health care system. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(22):2039-2046.